Objectives
- Describe the different models of communication.
- Distinguish similarities and differences between each model of communication.
- Determine the different advantages and disadvantages of different models of communication.
Models of Communication
- Models are used to visually demonstrate how interactions between different components in communication work.
- There are three types of models of communication:
- Linear
- Transactional
- Interactive
Linear Model of Communication
Linear Model
- It is a one-way communication.
- It is used for mass communication.
- While senders send messages, receivers only receive.
- It has no concept of feedback and noise
- It has several defined components:
- Sender: the person who sends the message after encoding.
- Encoding: the process of converting the message into codes compatible with the channel and understandable by the receiver.
- Decoding: the process of changing coded message into understandable language by the receiver
- Message: the information sent by the sender.
- Channel: the medium which the message is sent.
- Receiver: the person who gets the message.
- Noise: the disruptions caused in the communication process in channel or in the ability to understand the message.
- There are also advantages and disadvantages of this model:
- Advantages:
- Good at audience persuasion and propaganda setting.
- It can produce intentional results.
- Disadvantages:
- Communication is not continuous.
- This is because there is no concept of feedback.
- There is no way to know if communication was effective.
- Communication is not continuous.
- Advantages:
Different Types of Linear Models
Lasswell’s Model
- It was developed by Harold D. Lasswell in 1948.
- It is also known as:
- action model
- linear model
- one-way model
- It is the one of the most influential models.
Aristotle’s Model
- The first and earliest linear model
- It was developed by Aristotle.
- He was a teacher of rhetoric.
- He also put up an academy to produce good speakers.
Berlo’s SMCR Model
- It was postulated by David Berlo in 1960.
- It came from Shannon-Weaver’s Model of Communication
- This model has some unique features:
- It contains factors individual components of communication making communication more efficient
- It focuses on:
- encoding before sending the message, and
- decoding before receiving the message.
- Some criticism of this model include:
- Both persons must be similar according to factors mentioned below.
- There is no concept of any feedback or communication barrier.
Shannon-Weaver’s Model
- It has no concept of feedback.
- This model can only be used in public speaking.
Transactional Model of Communication
Transactional Model
- It is a two-way communication.
- There is an exchange of information.
- It is used for interpersonal communication (between persons).
- Senders and receivers each take turns to send and receive messages.
- We call both the sender and receiver as communicators.
- There is simultaneous feedback.
- The process of sending and receiving messages happens at the same time.
- Feedback is taken as a new message.
- There advantages and disadvantages of this model include:
- Advantages:
- There is simultaneous and instant feedback
- There is no discrimination between sender and receiver.
- Disadvantages:
- It encourages non-verbal communication.
- There is more noise.
- This is because communicators communicate at the same time.
- Advantages:
Barlund’s Model
- It was proposed by Dean Barlund in 1970.
- He says that sending and receiving messages happens simultaneously.
- Because of this, noise and feedback also happens simultaneously.
- It was further adapted as the General Transactional Model.
- It shifted the trend from linear model dynamic and the two-way models.
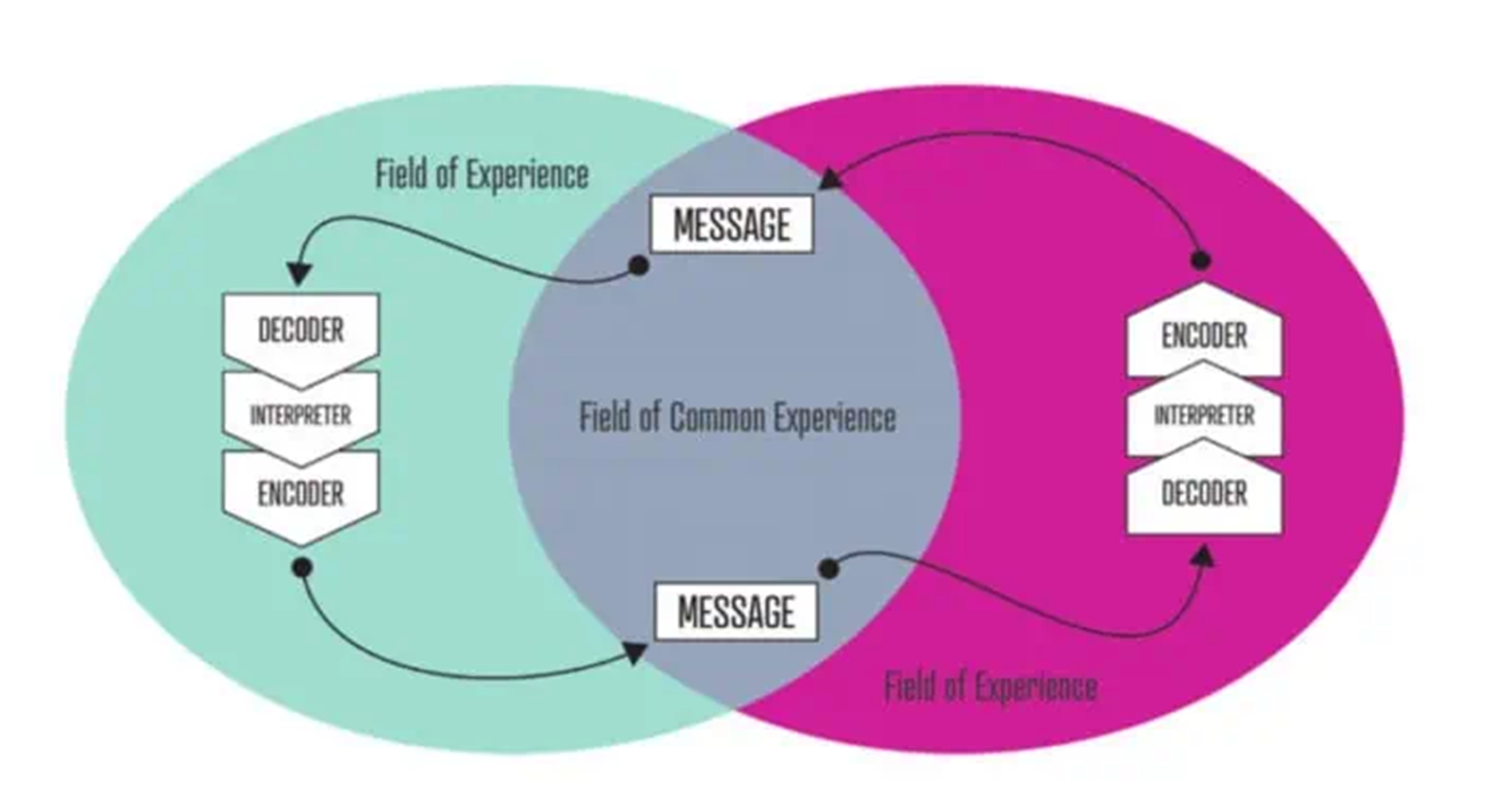
- It shows field experience of the sender and receiver.
- It is considered by critics as the most systematic model of communication.

Interactive Model of Communication
Interactive Model
- It is used for new media. (eg. the Internet)
- The feedbacks are often slower in turns.
- There is a concept of field of experience.
- It is also known as the convergence model.
- Communication becomes linear if receiver does not respond.
- There is no physical engagement between sender and receiver in communication.
- Here are some of its advantages and disadvantages:
- Advantages:
- There is feedback even in mass communication.
- New communication channels become possible.
- Disadvantages
- Feedback might take a very long time.
- Sender and receiver might not know each other.
- Advantages:
Schramm’s Model
- It was established by Wilbur Schramm
- He was also considered as Father of Mass Communication.
- He says that communication can only take place if and only if there is an overlap between the field of experience of both the speaker and the listener.
- The field of experience are the factors that influence our understanding and interpretation of the message:
- These can be:
- culture,
- social background,
- beliefs,
- experiences,
- values, and
- rules
- Some advantages of this model include:
- It allows both parties to give their opinion.
- This is because of circular communication.
- The interchanges between sender and listener is equally active.
- The concept of field of experience helps understand the communication process.
- It allows both parties to give their opinion.